How Pagination Affects Crawlability and What to Do About It
Pagination, a web design technique that divides content across multiple pages, can affect crawlability and SEO if not handled properly. It helps users navigate large amounts of information but poses challenges for search engines.
Key issues include fragmented content, duplicate content, and inefficient use of crawl budget, which can prevent complete indexing and reduce SEO performance. To improve crawlability, use self-referencing canonical tags, implement crawlable anchor links, and exclude paginated pages from XML sitemaps.
Best practices also include using rel=”next” and rel=”prev” tags, maintaining clean URLs, and optimizing meta tags. Alternatives like infinite scroll or load more buttons require careful implementation to ensure search engines can access all content.
Regular monitoring with tools like Google Search Console and conducting SEO audits are crucial for maintaining optimal crawlability and avoiding common mistakes. Balancing user experience with SEO needs is essential for effective pagination.
Understanding Pagination
Pagination is a common web design element that organizes content across multiple pages, making it easier for users to navigate large volumes of information. However, when it comes to search engine optimization (SEO), pagination can present significant challenges, particularly in terms of crawlability.
Understanding these challenges and implementing effective strategies can greatly enhance your site’s SEO performance.
What is Pagination?
Pagination refers to the process of dividing a large set of content into discrete pages. This is typically seen in blog archives, product listings in e-commerce, and search results pages.
Pagination helps improve user experience by breaking down extensive information into manageable chunks, allowing users to browse through content without feeling overwhelmed.
Common Uses of Pagination in Web Design
Pagination is widely used across various types of websites. In blogs, it separates posts by date or category.
In e-commerce sites, it organizes products, making it easier for customers to find what they are looking for. Search engines also use pagination to display results over several pages, enhancing usability.
How Pagination Affects Crawlability
The Challenges of Paginated Content for Crawlers
Pagination can create several challenges for search engine crawlers. These include:
- Fragmented Content: Bots might not follow all paginated links, leading to only a subset of your content being indexed.
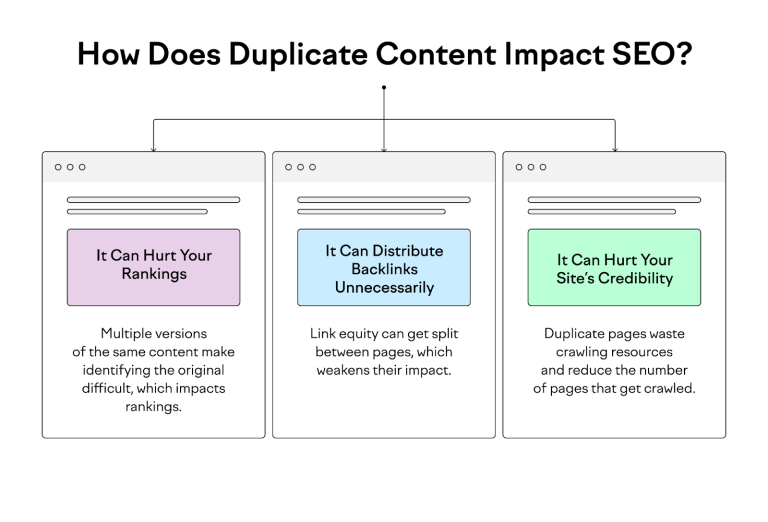
- Duplicate Content: If not managed correctly, pagination can create duplicate content issues, confusing search engines and diluting ranking power.
- Inefficient Crawling: Crawlers might waste resources by repeatedly indexing pages with minimal changes, reducing the crawl budget for more important pages.
Case Studies: Examples of Pagination Issues
Consider an e-commerce site with thousands of products spread across hundreds of paginated pages. If the pagination is not correctly implemented, search engines might index only the first few pages, leaving a vast amount of content unindexed.
Another example is a blog where older posts get buried under multiple paginated layers, making it difficult for crawlers to reach and index them.
Technical Insights into Pagination
How Search Engine Crawlers Interpret Pagination
Search engine crawlers use various signals to interpret pagination. These include HTML tags like rel=”next” and rel=”prev”, which indicate the relationship between paginated pages. Properly implementing these tags helps crawlers understand the sequence of paginated content, ensuring they follow and index all pages correctly.
HTML and Pagination: Best Practices
Using semantic HTML is critical for effective pagination. Best practices include:
- Rel=”next” and Rel=”prev” Tags: These tags help crawlers understand the order of paginated pages.
- Canonical Tags: Use canonical tags to indicate the preferred version of a page, reducing duplicate content issues.
- Clean URLs: Ensure your paginated URLs are simple and descriptive, making them easier for both users and crawlers to understand.
Best Practices for Pagination and SEO
Implementing Rel=”next” and Rel=”prev”
The rel=”next” and rel=”prev” tags are essential for pagination. They signal to search engines the order of pages, helping bots navigate through your content seamlessly. Implementing these tags correctly ensures that all your paginated content gets crawled and indexed efficiently.
Using Canonical Tags with Pagination
Canonical tags are crucial for managing duplicate content in pagination. By setting a canonical URL for each paginated series, you indicate the main page to be indexed, consolidating ranking signals and avoiding duplicate content penalties.
The Role of XML Sitemaps in Pagination
XML sitemaps provide a roadmap of your site for search engines. Including all paginated pages in your sitemap ensures that crawlers are aware of their existence, improving the chances of them being indexed. This is especially important for large sites with extensive paginated content.
Alternative Approaches to Handling Pagination
Infinite Scroll vs. Pagination
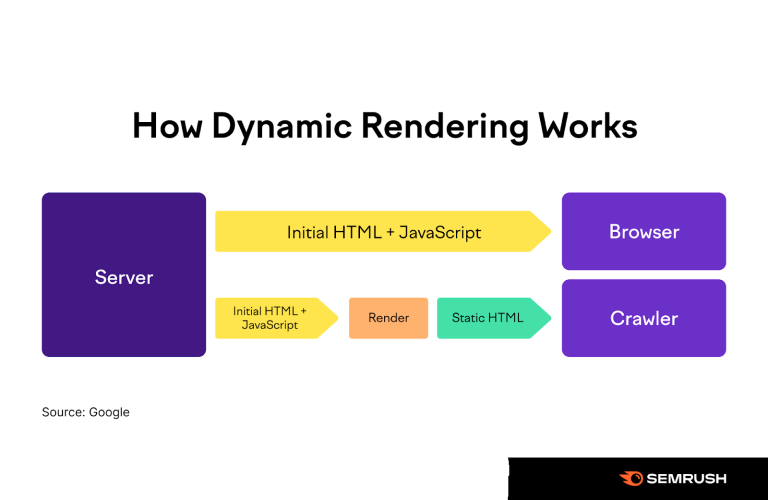
Infinite scroll dynamically loads content as users scroll down the page, offering a seamless browsing experience. However, it can be challenging for search engines to crawl, as they might not trigger the necessary loading actions.
Proper implementation, including using hybrid approaches combining infinite scroll with paginated URLs, can mitigate these issues.
Load More Buttons: Pros and Cons
Load more buttons are another alternative to traditional pagination. They allow users to load additional content without navigating to a new page.
This method can improve user experience but, like infinite scroll, requires careful implementation to ensure that all content is accessible to search engines.
Improving User Experience with Pagination
Balancing User Experience and SEO
Effective pagination balances user experience and SEO needs. Ensure that pagination controls are easy to use and visible, providing clear navigation cues. Simultaneously, implement technical SEO best practices to maintain crawlability and indexability.
Case Studies: Effective Pagination Implementations
Examining successful examples of pagination can provide valuable insights. For instance, large e-commerce sites like Amazon use numbered pagination combined with clear navigation and SEO-friendly URLs.
Blogs with extensive archives often implement chronological pagination, making it easy for both users and search engines to follow the content flow.

Common Mistakes to Avoid
Misusing Noindex and Nofollow Tags
Misusing noindex and nofollow tags can harm your SEO. While these tags can prevent certain pages from being indexed, overusing them can result in important content being missed by search engines. Use these tags sparingly and strategically.
Ignoring User Experience in Pagination Design
Focusing solely on SEO while neglecting user experience can be detrimental. Ensure that your pagination design is intuitive and user-friendly, encouraging visitors to explore more of your content while maintaining good SEO practices.