Best practices for managing duplicate content to enhance crawlability.
How does duplicate content affect SEO? Duplicate content confuses search engines, potentially leading to lower rankings or penalties. It also wastes crawl budget by consuming resources on multiple versions of the same content.
Effective management through strategies like canonical tags and 301 redirects helps consolidate duplicate URLs and improves overall SEO performance.
Managing duplicate content is a critical aspect of SEO often overlooked by website owners. Duplicate content, which refers to identical or substantially similar content appearing on multiple URLs, can significantly impact your website’s crawlability and search engine rankings.
Effective management not only maintains your site’s integrity but also enhances its crawlability, ensuring search engines can efficiently index your pages.
Duplicate content can manifest in various forms, such as exact duplicates or near duplicates with minor variations in phrasing or parameters. Causes include URL parameters used for tracking or sorting, session IDs generating unique URLs, and separate printer-friendly versions of pages.
The content syndication across multiple sites without proper management can also lead to duplication issues.
Definition and Types of Duplicate Content
Duplicate content is content that appears on more than one web page, either within the same website or across different websites. This can occur in various forms, such as:
- Exact Duplicates: Identical content that is copied verbatim.
- Near Duplicates: Content that is very similar but has minor differences, such as variations in phrasing or keywords.
Causes of Duplicate Content
URL Parameters
URL parameters, often used for tracking or sorting, can create multiple versions of the same content. For example, URLs like example.com/page?sort=asc and example.com/page?sort=desc might show the same content but are treated as different pages by search engines.
Session IDs
Session IDs are another common cause of duplicate content. When a new session ID is generated for each visitor, it can create unique URLs for the same content, leading to duplication.
Printer-friendly Versions
Creating separate printer-friendly versions of web pages can result in duplicate content if not handled correctly. These versions need to be properly managed to avoid indexing by search engines.
Syndicated Content
Republishing content from other sources or having your content republished on multiple sites can also lead to duplication. While syndication can broaden your reach, it needs careful management to avoid SEO issues.
Impact on SEO and Crawlability
Search Engine Penalties
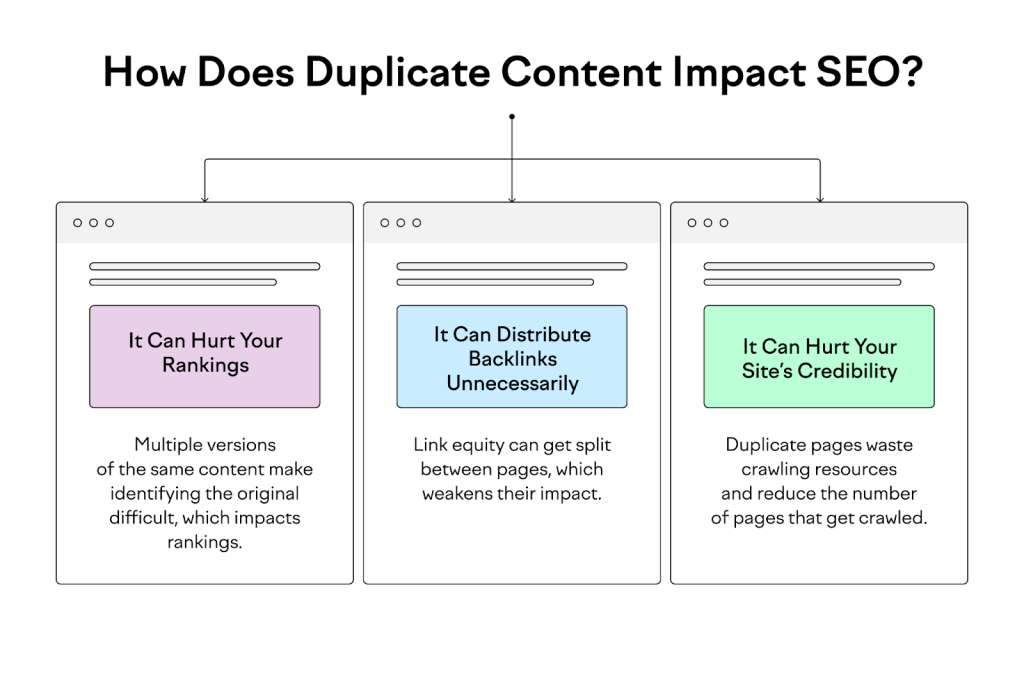
Search engines strive to provide the best possible user experience by delivering unique and relevant content. Duplicate content can confuse search engines and result in lower rankings or penalties. If search engines cannot determine the original source of content, they might not rank any of the pages well.
Reduced Crawl Efficiency
Duplicate content can waste valuable crawl budget. Search engine bots have a limited amount of resources to crawl your site, and duplicate pages can consume these resources unnecessarily, preventing other important pages from being indexed.
Identifying Duplicate Content
Using Google Search Console
Google Search Console is a powerful tool for identifying duplicate content. It provides insights into how Google crawls and indexes your site and can highlight issues related to duplicate content.
Third-party Tools
Several third-party tools, such as Screaming Frog, Copyscape, and SEMrush, can help identify duplicate content on your site. These tools offer comprehensive reports and actionable insights to address duplication issues.
Best Practices for Managing Duplicate Content
Canonical Tags
Using canonical tags is one of the most effective ways to manage duplicate content. A canonical tag tells search engines which version of a page is the preferred one to index. This helps consolidate duplicate pages and ensures the right version is ranked.
301 Redirects
Implementing 301 redirects is another effective strategy. This method permanently redirects one URL to another, indicating to search engines that a page has moved. It consolidates duplicate pages into a single URL, preserving link equity and improving crawl efficiency.
Meta Tags
Using meta tags like noindex can prevent search engines from indexing duplicate pages. This method is useful for pages that need to exist for user experience but shouldn’t appear in search results.
Preventing Duplicate Content
Consistent URL Structure
Maintaining a consistent URL structure helps prevent duplicate content. Ensure that your URLs are clean, descriptive, and avoid unnecessary parameters. Using a single domain and protocol (HTTP vs. HTTPS) consistently can also prevent duplication.
Avoiding Parameter Issues
Minimize the use of URL parameters, especially for tracking and sorting. When parameters are necessary, use URL rewriting to create clean, parameter-free URLs. Additionally, consider using the URL parameter tool in Google Search Console to indicate how parameters should be handled.
Content Syndication; Benefits and Risks
Content syndication can extend your reach and audience, but it also risks creating duplicate content issues. It’s crucial to manage syndicated content carefully to avoid negative impacts on SEO.
Rel=”canonical” for Syndicated Content
When syndicating content, use the rel=”canonical” tag to point to the original source. This tag tells search engines that the syndicated content is a copy and should be treated as a duplicate of the original.
Technical SEO Considerations
Robots.txt and Noindex
Use robots.txt to control which pages search engines can crawl. For pages that should exist but not be indexed, use the noindex meta tag. These technical controls help manage duplicate content and improve crawl efficiency.
Sitemap Management
Ensure your sitemap only includes canonical URLs. Regularly update your sitemap to reflect the preferred versions of your pages and exclude duplicates. This helps search engines understand your site structure and index the right content.
Monitoring and Auditing: Regular Content Audits
Conduct regular content audits to identify and address duplicate content issues. This involves reviewing your site’s content, checking for duplication, and implementing necessary fixes. Regular audits help maintain a healthy and crawlable site.
Several tools can assist in monitoring duplicate content. Google Search Console, Screaming Frog, SEMrush, and Ahrefs provide features to track and manage duplication issues, ensuring your site remains optimized for search engines.
FAQs
What is duplicate content? Duplicate content refers to identical or substantially similar content appearing on multiple URLs within the same website or across different websites.
How does duplicate content affect SEO? Duplicate content can confuse search engines, leading to lower rankings or penalties. It also wastes crawl budget, preventing other important pages from being indexed.
What are canonical tags? Canonical tags are HTML elements that help search engines identify the preferred version of a page among duplicates, consolidating link equity and improving crawl efficiency.
How can I prevent duplicate content? Prevent duplicate content by maintaining a consistent URL structure, minimizing URL parameters, and using technical SEO practices like canonical tags and 301 redirects.
What tools can help identify duplicate content? Tools like Google Search Console, Screaming Frog, Copyscape, SEMrush, and Ahrefs can help identify and manage duplicate content on your site.
Why is managing duplicate content important? Managing duplicate content is essential for maintaining your site’s integrity, enhancing crawlability, and improving overall SEO performance.